THE AVERAGE ACCOUNTING RETURN (AAR)
AAR=Average net income/Average book value
Average book value or average investment can be exchanged
Project Decision:
- AAR > target AAR, so accept the project
- AAR < target AAR, so reject the project
Advantages for Average Accounting Return (AAR):
- Easy to calculate
- Needed information will usually be available.
Disadvantages for Average Accounting Return (AAR):
- Not a true rate of return; time value of money is ignored.
- Uses an arbitrary benchmark cutoff rate.
- Based on accounting (book) values, not cash flows and market values.
Example:
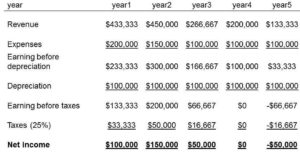
Company is evaluating whether buy a store in a new mall or not. The purchase price is $500,000. We will assume that the store has an estimated life of five years and will need to be completely scrapped or rebuilt at the end of that time. The projected yearly sales and expenses figures are shown below:
You are required to evaluate the project if company wants target average accounting return of 15%.
Solution:
Average net income=(100,000+150,000+50,000+0-50,000)/5 = $50,000
Average Book Value=(500,000+400,000+300,000+200,000+100,000+0)/6=$250,000
AAR=Average net income/Average book value=$50,000/250,00= 20%
The firm has a target AAR of 15% less than 20%, then this investment is acceptable.
Source:
- Phnom Penh HR
- Mcgraw-Hill – Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance